Ijraset Journal For Research in Applied Science and Engineering Technology
- Home / Ijraset
- On This Page
- Abstract
- Introduction
- Conclusion
- References
- Copyright
Impact of CSR Activities on the Enhancement of Income of Farmers in Sustainable Agriculture
Authors: Banusri M, Bharath H, Guruprasad K. G, Dr. Amalanathan P.
DOI Link: https://doi.org/10.22214/ijraset.2023.56237
Certificate: View Certificate
Abstract
Sustainable agriculture is the practice of farming in a way that satisfies society\\\'s current demands for food and textiles without affecting the ability of present or future generations to meet their own needs. The article focuses on agricultural businesses that, due to huge financial risks, are unable to provide goods of high quality for society, which results in less sustainable agriculture. The goal of this paper is to identify ways to manage the financial risks of agricultural entrepreneurship based on its corporate social responsibility for sustainable development and the delivery of food security. This paper also focuses on the security and affordability of the product, which cannot be done due to financial risks.
Introduction
I. INTRODUCTION
Three primary objectives are incorporated into the work of sustainable agriculture practitioners: a healthy environment, financial success, and social and economic equality. Growers, food processors, distributors, retailers, consumers, and waste managers are just a few of the people who can contribute to a sustainable agricultural system. People who work in sustainable agriculture and sustainable food systems use a variety of approaches. Growers can employ techniques to improve soil health, use less water, and reduce farm pollution. Customers and merchants who are concerned about sustainability may look for "values-based" goods that are made in a way that supports the welfare of farmworkers, is not harmful to the environment, or boosts the local economy. Agroforestry Biofuels, Conservation Tillage, Controlled Environment Agriculture (CEA), Cooperatives, Cover Crops, Dairy Waste Management, and others are a few topics related to sustainable agriculture. Farmers will use less chemicals, rely less on nonrenewable energy sources, and conserve limited resources by using sustainable methods. When you take into account the expanding population and the need for food, maintaining the health and replenishment of the soil can go a long way. This paper focuses primarily on bringing in good products via sustainable agriculture through corporate social responsibilities. Agriculture entrepreneurs are the ones who must give good quality seeds and products to the consumer. Also illustrates how corporate social responsibility may be used to decrease excessive financial risk.
A. Objectives
- To study the different risks faced by the farmers in involving sustainable agricultural activities
- To know the corporates that are interested in financing sustainable agriculture through CSR activities.
- To assess the growth and development of farmers involved in sustainable agriculture through CSR `activities
B. Methodology
The data used for the study is based on primary data, which is collected from the selected corporates and sample of farmers chosen for the study The primary data are collected through two different questionnaire for corporates and farmers by using google form. The collected data are processed and analyzed with the help of statistical tool, regression.
II. LITERATURE REVIEW
- Kuldeep Singh,et.al, This paper explores the intricate relationship between Corporate Social Responsibility (CSR), organizational performance, sustainability risk management, and organizational reputation. Existing literature suggests that CSR activities can significantly impact organizational performance by enhancing stakeholder trust and commitment, as well as fostering long-term value creation. However, the extent and nature of this impact are contingent upon various factors, one of which is sustainability risk management. The literature underscores the importance of proactively managing sustainability risks to mitigate potential adverse effects on an organization's financial and operational performance. Additionally, the paper highlights the role of organizational reputation as a key mediator in this relationship, as a positive reputation can enhance the effectiveness of CSR initiatives and risk management efforts, thereby further contributing to superior organizational performance. This research aims to provide valuable insights into the dynamic interplay of these factors and offer a holistic understanding of how CSR, sustainability risk management, and organizational reputation jointly influence an organization's performance.
- Liu Wang, Yong Wang (May 2023)The question of whether Corporate Social Responsibility (CSR) holds greater significance in disrupted industries has garnered substantial attention in the literature. Scholars have posited that in industries marked by rapid technological advancements, changing consumer preferences, and heightened competition, CSR initiatives can offer distinct advantages. These sectors often face heightened scrutiny, and consumers are increasingly looking to align with companies that exhibit a commitment to sustainability and responsible business practices, which can be leveraged for competitive differentiation. Several studies have indicated that proactive engagement in CSR can help disrupted industries build resilience, mitigate reputational risks, and attract both customers and investors. Moreover, CSR can play a pivotal role in facilitating strategic partnerships and fostering innovation, which are vital for adaptation and success in turbulent environments. This paper seeks to contribute to the ongoing discourse by delving deeper into the relationship between CSR and disrupted industries, offering a comprehensive analysis of how and to what extent CSR can provide a competitive edge in these dynamic business landscapes.
- Liudmila Khoruzhy,et.alThe literature increasingly emphasizes sustainable development in agriculture, highlighting the role of management accounting. Agricultural enterprises, often resource-intensive and eco-sensitive, face mounting pressure for active environmental engagement. Past research demonstrates that integrating environmental considerations into accounting practices yields cost-efficiency, resource optimization, and regulatory compliance benefits. This paper explores inter-organizational management accounting in sustainable agriculture, examining how enterprises collaborate with stakeholders to monitor and reduce their environmental impact while promoting sustainability across the agricultural value chain. The study reveals the transformative potential of inter-organizational management accounting in driving agricultural sustainability, enhancing our understanding of the complex relationship between financial performance, environmental responsibility, and stakeholder collaboration in this sector.
- Benjamin S.Thompson, The literature highlights the rising interest in impact investing for biodiversity conservation, particularly using bonds. Recognizing the urgency of global biodiversity loss, there's a growing acknowledgment of finance's vital role in addressing this issue. Prior research emphasizes the potential of impact bonds to attract private capital, offering financial returns and measurable environmental benefits. These bonds align investor interests with conservation objectives, supporting projects that counter biodiversity loss, protect endangered species, and restore ecosystems. However, complexities, financial risks, ecological uncertainties, and the challenge of quantifying environmental impacts are recognized. This paper contributes by analyzing the financial and environmental risks associated with impact investing in biodiversity conservation through bonds, offering insights into their effectiveness in balancing investor interests with urgent conservation needs.
- Hafiz Mohkum Hammad, et.al, The COVID-19 pandemic has triggered a wave of research exploring its multifaceted impacts on the environment, society, and food security. As governments worldwide implemented various containment measures, including lockdowns and travel restrictions, to curb the virus's spread, significant environmental consequences were observed. These included temporary reductions in air pollution and carbon emissions due to decreased industrial activity and transportation, revealing the potential for a more sustainable post-pandemic recovery. On the societal front, the pandemic exacerbated existing inequalities, affecting vulnerable populations disproportionately. It exposed weaknesses in healthcare systems, social safety nets, and access to education. Food security became a critical concern, with disruptions in supply chains, income loss, and reduced access to nutritious food. This paper builds on this literature by providing a comprehensive analysis of the multifaceted impacts of the COVID-19 pandemic on the environment, society, and food security, aiming to offer valuable insights into the need for resilient and sustainable systems in the face of global crises.
- Charity Aremu, The literature on agricultural productivity as a pivotal component of inclusive growth and food security underscores its fundamental role in addressing the global challenge of feeding a growing population while reducing poverty and inequality. Agriculture, particularly in developing economies, serves as a vital source of livelihood for a significant portion of the population. Enhanced agricultural productivity not only ensures a more stable and affordable food supply but also generates income opportunities and employment, particularly for marginalized rural communities. It promotes inclusive growth by reducing poverty, improving living standards, and fostering economic resilience.
However, the literature also acknowledges the multifaceted challenges, including resource constraints, climate change impacts, and the need for sustainable agricultural practices, that must be addressed to harness the full potential of agricultural productivity in achieving food security and inclusive growth. This paper seeks to contribute by delving into the complex relationship between agricultural productivity, inclusive growth, and food security, offering insights into strategies and policies that can optimize this connection to ensure a sustainable and equitable global food system.
7. PanelBo Zhu, et.al, Recent scholarly attention has increasingly focused on investigating systemic risk spillovers between the energy and agriculture sectors, especially in the context of financial and pandemic crises. Scholars have highlighted the intricate interdependencies and vulnerabilities that exist between these sectors, with energy prices impacting agricultural production costs and disruptions in agriculture affecting energy markets. While previous research has explored these relationships in different contexts, the interplay of financial crises and pandemic-induced shocks on these sectors remains relatively unexplored. This study addresses this research gap by conducting a comprehensive analysis of intersectoral systemic risk spillovers between energy and agriculture, with a particular emphasis on the financial and COVID-19 crises. The research aims to provide valuable insights into the vulnerabilities, interconnectedness, and resilience of these sectors, informing critical policy and risk management strategies in an era marked by unprecedented global challenges.
III. OPERATIONAL DEFINITIONS OF IMPORTANT TERMS USED IN THIS STUDY
A. Sustainable Agriculture
The activity of entrepreneurial endeavors and operations within the agricultural industry is referred to as agriculture entrepreneurship. It involves people or organizations that spot opportunities, innovate, and either start new agricultural enterprises or enhance those that already exist. Through the introduction of innovative concepts, technology, and business models, agriculture entrepreneurs play a significant part in modernizing and transforming the agricultural industry.
B. Agriculture Entrepreneurship
Agriculture entrepreneurship is crucial for the agricultural sector's continuous development and sustainability since it promotes innovation, raises productivity, and assists in overcoming industrial issues. Entrepreneurs in this industry encourage economic growth, environmental preservation, and food security
The following are some important characteristics of agriculture entrepreneurship and possible business ventures:
- Identifying Opportunities: In the early stages of their business plans, agriculture entrepreneurs frequently look for unmet needs, gaps, or openings within the agricultural value chain. This can entail determining the market's need for particular crops or goods, discovering inefficiencies in the production or distribution process, or coming up with creative solutions to environmental or sustainability issues.
- Innovation: Innovation is a component of agricultural entrepreneurship. Entrepreneurs may create new technologies, methods, or procedures that increase output, reduce expenses, or raise the quality of agricultural products. Crop cultivation, wildlife management, and food processing are only a few examples of the diverse applications for this breakthrough.
- Starting New Ventures: Agribusiness owners may start brand-new enterprises from scratch. This can entail founding a farm, an agribusiness, or a startup for agricultural technologies.
- Value Addition: Agriculture entrepreneurs frequently concentrate on enhancing the value of their products. This may entail changing agriculturally produced raw materials—such as fruits into jam or milk into cheese—into finished goods. Higher profitability and market distinction can result from adding value.
- Technology Adoption: Agriculture entrepreneurs are leading the way in embracing and incorporating technology into farming methods. To improve crop management, reduce resource wastage, and boost yields, this includes using sensors, drones, automation, and data analytics.
- Sustainable Agriculture: A lot of farmers are dedicated to using environmentally friendly and sustainable farming methods. They might create and use organic farming practices, promote biodiversity, and engage on initiatives for conservation and resource management.
- Market Access: Agriculture entrepreneurs frequently strive to make it easier for farmers to access markets. This could entail setting up farmer cooperatives, building new distribution methods, or developing internet platforms that link producers and consumers.
- Education and Training: Some agricultural entrepreneurs concentrate on giving farmers information and training. To assist farmers in developing their abilities and implementing best practices, they might provide workshops, online courses, or consultancy services.
- Agri-Tourism: Some agricultural business owners engage in agri-tourism by inviting visitors onto their properties, providing farm-to-table dining experiences, or developing tourist attractions with an agricultural theme.
- Policy Advocacy: Agricultural entrepreneurs may also participate in policy lobbying to advance beneficial laws and rules that encourage agricultural innovation and entrepreneurship.
C. How the Sustainable Agriculture Evolved
In response to diverse environmental, social, and economic difficulties, sustainable agriculture has changed over time.
Its evolution can be followed through a number of crucial phases:
- Traditional and Subsistence Agriculture: Agriculture was primarily dependent on traditional and subsistence methods for a large portion of human history. Farmers raised crops and livestock for their communities using local knowledge and traditional ways. While having negligible environmental impact, these techniques frequently had low output.
- Industrial Agriculture: The 20th century brought the beginning of the industrialization of agriculture, which brought about enormous changes. Growing populations could now be maintained with the help of technological advancements including the creation of synthetic fertilizers and pesticides, mechanization, and irrigation. But during this time, worries about soil erosion, water pollution, and biodiversity loss as a result of monoculture farming and extensive chemical use also began to surface.
- Environmental Movement: The environmental movement began to gain momentum in the 1960s and 1970s, when conventional agriculture's negative consequences were becoming more widely known. Calls for more environmentally friendly and sustainable farming methods have been driven by worries about pollution, habitat damage, and food safety.
- Organic Farming and Certification: As a result of the detrimental impact that conventional agriculture has on the environment and human health, organic farming has become more popular. Consumers now have a means of recognizing and supporting more environmentally friendly farming methods thanks to the introduction of organic standards and certification programs.
- Local Food Movements: The local food movement drove customers to support regional farmers and sustainable farming methods in the late 20th and early 21st centuries. Community-supported agriculture (CSA) initiatives, farmers' markets, and farm-to-table eateries all gained popularity.
- Technological Developments: The development of sustainable agriculture has been aided by technological advancements. Farmers can now use resources more efficiently, create less waste, and make more informed decisions thanks to precision agriculture, genetic engineering, and data-driven methods.
- Climate Change and Resilience: As the effects of climate change on agriculture become more widely recognized, techniques for fostering resilience have been developed. In order to be sustainable, agriculture must now put more attention on lowering greenhouse gas emissions and climate change adaptation.
- Global Initiatives: Sustainable agriculture is now a top focus on a global scale, with programs like the Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) of the United Nations targeting global issues including food security, poverty eradication, and sustainable farming techniques.
As new challenges and chances materialize, sustainable agriculture keeps changing. The complex and linked challenges of food production, environmental preservation, and equitable society are still being addressed in this dynamic field through constant research, innovation, and adaptation.
D. Financial Risk
When discussing sustainable agriculture, the term "financial risk" refers to the possibility of economic or financial difficulties or uncertainties that can have an impact on the viability and sustainability of agricultural practices and businesses. These hazards can come from a number of different places and affect both individual farmers and the larger agriculture industry.
Financial risks can have the following effects on sustainable agriculture:
- Market Price Fluctuations: The supply and demand, weather, and general economic conditions are some of the variables that frequently cause price volatility for agricultural products. During times of low market prices, farmers may experience decreased revenue and profitability, making it difficult to invest in sustainable practices or embrace technologies that could improve sustainability.
- Production Risks: Production risks include reduced crop yields or animal losses as a result of weather-related occurrences including droughts, floods, and extremely high temperatures. These production risks might alter farmers' income streams, making it challenging to recover their investments in environmentally friendly agricultural methods.
- Access to Capital: Sustainable agriculture frequently necessitates up-front expenditures in tools, techniques, and methods that may take some time to pay off financially. Farmers' ability to make these investments may be restricted by limited access to finance or credit, which would delay the adoption of sustainable practices.
- Input Cost Variability: Changes in the price of inputs like fuel, fertilizer, and pesticides can have an impact on how profitable a farmer gets. Reduced input utilization or more expensive organic inputs that may be prone to price variations may be part of sustainable agriculture.
- Risks Associated with policy and Regulation: The financial sustainability of sustainable practices can be impacted by changes in government policies or laws related to agriculture, land use, environmental conservation, or subsidies. For instance, cutting back on incentives for sustainable farming methods might make people less likely to use them.
- Access to Markets: Farmers using sustainable agriculture may have trouble reaching markets that will give them a premium for their products if they are produced sustainably. Market access restrictions may have an impact on sales and profitability.
- Consumer Preferences: Farmers may suffer financially as a result of shifting consumer demands for sustainably produced agricultural goods. Changing farming practices may be necessary to satisfy these tastes, which might be expensive.
- Climate Change and Environmental Risks: Environmental risks brought on by climate change are addressed via sustainable agriculture. However, because they harm crops, interfere with business operations, and necessitate more expensive adjustments, extreme weather events and climate-related risks can present farmers with financial difficulties.
- Supply Chain Disruptions: The COVID-19 outbreak brought attention to the weaknesses in the agricultural supply systems. Farmers' capacity to sell their goods and get payments can be affected by disruptions, which can have a negative influence on their financial security.
- Currency Exchange Rates: For farmers engaged in international trade, changes in exchange rates can have an impact on export profits and import expenses, which can have an impact on overall financial performance.
Farmers, decision-makers, and other stakeholders can think about a variety of methods to mitigate these financial risks and advance sustainable agriculture, such as:
- Agritourism or the diversification of revenue sources through value-added products.
- Improving resilience through insurance and risk management techniques.
- Expanding farmers' access to financial resources and financial knowledge.
- Encouraging policies and rewards that encourage sustainable practices.
- Increasing market access and stimulating demand for products made with sustainable practices.
- Encouraging research and extension programs that assist farmers in implementing affordable sustainable practices.
In general, financial risk management is crucial for the long-term sustainability and success of agricultural firms that want to implement and uphold sustainable practices.
E. Why Companies do CSR Towards Sustainable Agriculture
Businesses take part in CSR programs aimed at promoting sustainable agriculture for a number of reasons:
- Impact on Society and Environment: Local communities and the environment can benefit from sustainable agricultural methods. In sustainable agriculture, corporate social responsibility (CSR) can result in less environmental damage, the preservation of natural resources, and improved farmer incomes.
- Reputation & Brand Image: Customers tend to have positive opinions of businesses that promote sustainable agriculture. A company's reputation and brand image can be improved by showcasing a commitment to sustainability; this can result in a rise in consumer loyalty and trust.
- Regulatory Compliance: There are laws governing social and environmental obligations in many nations. Companies can comply with these requirements and minimize legal and reputational risks by participating in corporate social responsibility activities connected to sustainable agriculture.
- Long-Term Business Viability: Many businesses, especially those in the food and beverage, retail, and agricultural sectors, depend on the sustainability of agriculture for their long-term survival. Businesses whose supply chains are dependent on agriculture need to make sure they have a reliable source of raw materials.
- Resilient Supply Chains: Resilient supply chains can result from sustainability activities. Supply chains may be disrupted by environmental degradation and climate change, but businesses that engage in sustainable agricultural methods are better equipped to handle these changes.
- Cost Savings: Over time, sustainable farming methods frequently result in cost savings. Production costs can be lowered, for instance, through increased soil health, decreased waste, and more effective use of resources.
- Market Access and Competitive Advantage: Products originating from sustainable agriculture are preferred by certain markets and consumers. Companies can reach these markets and obtain a competitive edge by participating in sustainability-related CSR projects.
- Relationships between Investors and Shareholders: A growing number of investors and shareholders are worried about social and environmental responsibilities. Proactive CSR initiatives make a company more attractive to ethical investors, which can lead to better access to financing and a higher stock price.
- Possibilities for Innovation and Research: Participating in CSR projects pertaining to sustainable agriculture might stimulate innovation and research. Businesses may make investments in the creation and application of innovative techniques and technology that enhance agricultural sustainability, thereby opening up new sources of income.
- Stakeholder Engagement: By interacting with stakeholders, such as farmers and local communities, businesses can reduce tensions, forge stronger bonds, and win support for their operations.
Sustainable agriculture-related corporate social responsibility (CSR) efforts can benefit businesses, the environment, and society as a whole. They can help the company's reputation, resilience, and long-term sustainability in addition to promoting favorable social and environmental consequences.
F. How CSR Acted upon Reducing Financial Risk for Sustainable Agriculture
Corporate social responsibility (CSR) is the idea that businesses should voluntarily assume obligations that go above and beyond what is required by law to support social and environmental goals. Although CSR initiatives frequently relate to the commercial sector, they can indirectly influence sustainable agriculture and help farmers and agricultural enterprises manage their financial risks. Here are some ways that corporate social responsibility (CSR) initiatives can help to lower the financial risk associated with sustainable agriculture:
- Supporting Sustainable Farming Methods: Many businesses that participate in CSR initiatives offer farmers financial and technical assistance to help them adopt sustainable farming methods. This aid might come in the form of instruction, materials, and help putting eco-friendly and resource-efficient practices into practice. Companies can help improve agricultural sustainability and lower the hazards related to unsustainable practices by doing this.
- Value Chain Engagement: Various stakeholders in the agricultural value chain, from suppliers to producers to consumers, may be engaged by businesses. Companies can open new markets for agricultural products made with sustainability in mind through ethical sourcing and supply chain management. By maintaining steady demand and maybe enabling them to earn higher prices for their sustainable products, this can help farmers lower their financial risks.
- Research and Innovation: Some CSR projects involve attempts to develop new agricultural technology and solutions through research and development. Companies can assist farmers in gaining access to cost- and resource-efficient technology, lowering production risks, and enhancing financial stability through funding research in sustainable agriculture.
- Access to Finance: Businesses involved in CSR initiatives may collaborate with financial institutions to make it easier for farmers to access financing and other financial services. Farmers who have access to financing can invest in infrastructure and sustainable practices, lowering adoption costs.
- Risk Reduction and Insurance: Businesses can work with insurers to create and market insurance products that are especially suited to handle the monetary risks connected with sustainable agriculture. These insurance options can shield farmers from financial loss caused by adverse weather conditions, pest outbreaks, or market swings.
- Building Capacity: CSR projects frequently require activities that help farmers and agricultural communities build their capacities. Training programs can help farmers become more skilled, knowledgeable, and resilient in the face of obstacles, such as threats to their finances.
- Environmental Stewardship: Environmental stewardship and conservation are emphasized in many CSR programs. Companies indirectly help to lower environmental risks that can influence agriculture, such as soil erosion, water scarcity, and climate-related hazards, through supporting reforestation projects, biodiversity conservation, and responsible land use.
- Community Development: In rural areas, CSR programs frequently place a high priority on community development. Companies can contribute to the improvement of the overall socioeconomic situation of farmers by making investments in infrastructure, education, healthcare, and livelihood opportunities in farming communities. This can lessen their financial risk as a result.
Programs for corporate social responsibility have a wide range of methodologies and aims, but they have a lot of potential to lower financial risks in sustainable agriculture. CSR initiatives can help create more resilient and financially secure agricultural systems by balancing company interests with sustainability objectives and community well-being.
G. Here are a few Examples of Sustainable Agricultural Methods and Procedures
- Organic Farming: Synthetic pesticides, herbicides, and fertilizers are not used in organic farming. Instead, it depends on organic matter, crop rotation, and natural inputs to enhance soil health and reduce negative effects on the environment.
- Crop Rotation: In a field, different crops are produced in different combinations from season to season. This procedure improves soil fertility, controls diseases and pests, and reduces soil erosion.
- No-Till Farming: By doing completely with or significantly reducing plowing and tilling, no-till farming minimizes soil disturbance. This method aids in carbon sequestration, erosion control, and moisture retention of the soil.
- Agroforestry: On the same plot of land, agroforestry blends trees or shrubs with crops or cattle. Through the sale of fruit or lumber from trees, this technique can increase biodiversity, improve soil fertility, and provide additional revenue.
- Cover Cropping: To prevent soil erosion, control weed growth, and supply organic matter, cover crops are sown in between main crop cycles. They lessen the demand for synthetic fertilizers by helping to fix nitrogen in the soil.
- Precision Agriculture: To maximize the use of inputs like water, fertilizer, and pesticides, precision agriculture uses technologies like GPS and remote sensing. This increases crop yields while decreasing waste and environmental effects.
- Integrated Pest Management (IPM): In order to effectively manage pests, integrated pest management (IPM) integrates biological, cultural, and chemical strategies. It places a focus on using biological controls while reducing the use of chemical pesticides.
- Rotational Grazing: To promote the natural regrowth of vegetation, rotational grazing includes moving cattle between several pastures. Through this method, overgrazing is avoided, soil erosion is decreased, and pasture health is increased.
- Drip Irrigation: Drip irrigation systems feed water directly to plant roots, minimizing water loss and increasing water efficiency in agriculture.
- Community-Supported Agriculture (CSA): CSAs let customers purchase products straight from local farmers. Subscribers get a portion of the farm's harvest, promoting regional farming and lowering the environmental impact of food distribution.
- Permaculture: Permaculture is a design concept that aims to make agricultural systems more like natural ecosystems. By including various plant and animal species, it promotes biodiversity, the health of the soil, and sustainability.
- Aquaponics: In a closed-loop system, aquaponics combines hydroponics (growing plants in water) and aquaculture (producing fish). A productive farming system is created when fish waste feeds plants with nutrients and plants clean the water for the fish.
- Conservation Tillage: By leaving crop leftovers on the field after harvest, conservation tillage procedures promote water retention and prevent soil erosion.
- Sustainable Livestock Management: Livestock management that is sustainable employs techniques including rotational grazing, adequate waste disposal, and careful use of antibiotics and hormones.
These are only a few instances of systems and practices for sustainable agriculture. Sustainable agriculture is versatile and adaptive, with farmers and other agricultural experts always coming up with and implementing cutting-edge methods to lessen environmental effects while fostering food security and economic success.
IV. HYPOTHESIS FORMULATION
- H0: The companies are not interested in financing sustainable agriculture through CSR
H1: The companies are interested in financing sustainable agriculture through CSR
2. H0: There is no growth of income to the farmers in sustainable agriculture through CSR activities
H1: There is a growth of income to the farmers in sustainable agriculture through CSR activities
V. ANALYSIS OF THE RESPONSES OF THE RESPONDENT:
Table 1 showing the responses of the respondents (farmers)
|
VARIABLES |
YES |
NO |
|
Have these CSR initiatives led to any measurable financial benefits or risk reduction for farmers or agricultural communities involved in your projects?
|
55.6% |
44.4% |
|
Have you observed any improvements in the financial stability or income of farmers who have participated in your sustainable agriculture programs?
|
52.4% |
47.6% |
|
Have CSR-supported programs helped you adopt sustainable farming practices that enhance your ability to cope with financial risks
|
53.2% |
46.8% |
|
Have you ever been involved in sustainable agriculture practices? |
58.7% |
41.3% |
|
Have you experienced any financial challenges or risks related to your sustainable agriculture activities? |
58.9% |
41.1% |
|
Have you faced income uncertainty due to any factors? |
55% |
45% |
|
Have you taken any specific measures or strategies to reduce the financial risks associated with sustainable agriculture? |
54% |
46% |
- Interpretation
The farmers had been asked for the response from the responded farmers over 58.7% percentage of farmers had been involved in sustainable agriculture practices
If we look into the farmers who have agreed that they are practicing sustainable agriculture they were divided into three categories 36.4% were following the practice for one year, 34.1% of them just started to follow 6 months ago and 29.5% of farmers were practicing it for 2 or more years
Half of the farmers were experiencing financial challenges or risks related to their sustainable agriculture activities and they also faced income uncertainty due to many factors
They had taken some specific measures or strategies to reduce the financial risks associated with sustainable agriculture and they also participated in some agricultural initiatives or programs that were supported by corporations with CSR initiatives focused on sustainability.
Only half of them agree agreeing the statement that CSR-supported programs helped them to adopt sustainable farming practices that enhanced their ability to cope with their financial risks
58.7% of farmers believe that CSR initiatives have contributed to improving their income stability and reducing financial risks associated with farming
Table 2 showing the responses of the respondents (corporates)
|
variable |
Yes |
No |
|
Has your organization been involved in supporting sustainable agriculture practices among farmers? |
66% |
34% |
|
Have you implemented any specific financial risk reduction strategies or programs to support farmers engaged in sustainable agriculture? |
69% |
31% |
|
Are there any notable success stories or case studies where financial risks were successfully mitigated through sustainable agriculture practices or support programs? |
55% |
45% |
|
Do you collect data or conduct assessments to measure the financial impact of sustainable agriculture on farmers, particularly in terms of risk reduction and income stability? |
56% |
44% |
|
Have you seen any changes in the finances of the farmers? |
51% |
69% |
- Interpretation
From the received response of organizations over 90.9% are involved in supporting sustainable agriculture practices from organizations and they have also implemented some specific financial risk reduction strategies or program to support farmers engaged in sustainable agriculture
Major percentage of financial assistance or tools provided by the farmers to manage financial risk in sustainable agriculture is credit which is over 38.3%, The next assistance or tools provided is Insurance which is around 33.3% and the rest 28.3% of them provided technical training.
It is agreed by most of them from the respondents that there are some notable success stories or case studies where financial risks were successfully mitigated through sustainable agriculture practices or support programs
The Organizations are stating that that they collect data or conduct assessments to measure the financial impact of sustainable agriculture on farmers, particularly in terms of risk reduction and income stability and most of the organizations have CSR initiatives related to sustainable agriculture.
Over 90.8% of them were saying that these CSR initiatives led to some measurable financial benefits or risk reduction for farmers or agricultural communities involved in their projects and they are also measuring the financial impact and risk reduction outcomes of your CSR initiatives in the context of sustainability agriculture.
Most of the organizations had also observed improvements in the financial stability or income of farmers who have participated in the sustainable agriculture programs. They have the data or case studies that demonstrate the positive financial outcomes or risk mitigation achieved through their CSR initiatives in agriculture and they have seen changes in the financial of the farmers.
A. Regression analysis
The following multiple regression table presents the coefficients and associated statistics for a model that predicts a specific outcome variable. Here are the interpretations based on the table:
Multiple R: The multiple correlation coefficient, 0.000197 & 2.01E-10 suggests a strong positive correlation between the independent variables included in the regression model and the dependent variable. This indicates that there is a tendency for the dependent variable to increase as the values of the independent variables increase collectively.
The obtained coefficient of determination (R-squared) is 0.000197 & 2.01E-10, which signifies that approximately 86% of the fluctuations in the outcome variable can be elucidated by the independent variables included in the model.
CSR-supported programs helped you adopt sustainable farming practices that enhance your ability to cope with financial risks
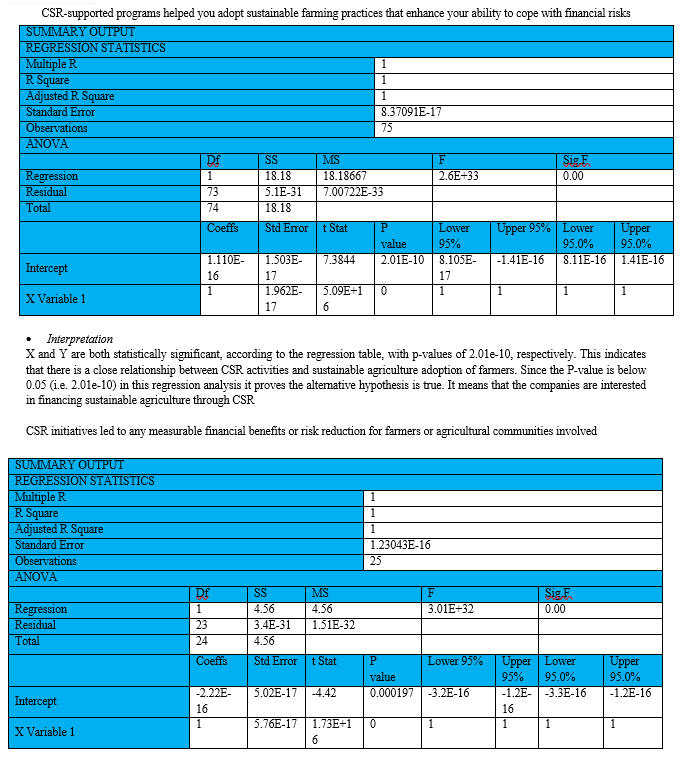
- Interpretation
The regression table shows that both X and Y are statistically significant, with p-values of 0.000197. This means that there is a significant positive relationship between sustainable agriculture and measurable increase in farmer’s income. Since the P-value is below 0.05 (i.e. 0.000197) in this regression analysis it proves the alternative hypothesis is true. It means that there is a growth of income to the farmers in sustainable agriculture through CSR activities
Conclusion
In conclusion, through this hypothesis we came to know that there is a impact in sustainable agriculture through CSR activities. With the regression table we can conclude that CSR activities show impact in sustainable agriculture and financial benefits of the farmers. Furthermore, the findings imply that CSR-backed projects benefit farming communities overall as well as individual farmers. Programs for corporate social responsibility that support financial risk management, more stable sources of revenue, and sustainable farming practices have a strong association that is backed by low p-values. By encouraging integrated pest management and cultivation of cover crops, for example, these programs reduce the need for expensive outside inputs and increase farmers\\\' tolerance to price shocks. Farmers can use the enhanced R-squared values to estimate the possible financial benefits and risk reduction associated with participating in CSR-supported projects with confidence, as the model is extremely trustworthy. Therefore, businesses that want to significantly improve the lives of farmers and agricultural communities should give priority to funding CSR projects that advance sustainability and financial stability. The statistical significance of the coefficients for X and Y confirms the presence of a strong and significant linkage, even though the regression table does not specify the precise strength of the relationship between income stability, risk reduction, and CSR-supported activities. The model\\\'s dependability is confirmed by the extraordinarily high R-squared values, which provide farmers with an instrument of confidence for calculating the advantages of CSR involvement. This thorough study emphasizes how CSR programs may assist the agriculture industry financially assist farmers, highlighting its significance for resilient and sustainable farming methods. Businesses looking to improve the lives of farmers and agricultural communities should think about investing in CSR as a smart way to accomplish these objectives. By the hypothesis, we came to know that there is a significant rise in increase the income of farmers. Through financial assistance, there is a way of strengthening sustainable agriculture.
References
[1] Kuldeep Singh (Faculty of Management Studies, CMS Business School, Jain (Deemed-to-be University), Bengaluru, India) , Linking CSR and organizational performance: the intervening role of sustainability risk management and organizational reputation, Social Responsibility Journal ISSN: 1747-1117 [2] Liu Wang, Yong Wang (May 2023) Is corporate social responsibility more valuable in disrupted industries?, ISSN: 0307-4358 May 2023 [3] Liudmila Khoruzhy - Sustainable Development of Agricultural Enterprises with an Active Environmental Stance: Analysis of Inter-Organizational Management Accounting, https://doi.org/10.55908/sdgs.v11i3.386 [4] Benjamin S. Thompson - Impact investing in biodiversity conservation with bonds: An analysis of financial and environmental risk, https://doi.org/10.1002/bse.3135 Volume32, Issue1 [5] Hafiz Mohkum Hammad, Charity Aremu - Impacts of COVID-19 pandemic on environment, society, and food securityAgricultural Productivity: A Key Component of Inclusive Growth Towards Food Security, Environmental Science and Pollution Research [6] Renda Lin - Intersectoral systemic risk spillovers between energy and agriculture under the financial and COVID-19 crises [7] PanelBo Zhu a, Renda Lin a - Intersectoral systemic risk spillovers between energy and agriculture under the financial and COVID-19 crises
Copyright
Copyright © 2023 Banusri M, Bharath H, Guruprasad K. G, Dr. Amalanathan P.. This is an open access article distributed under the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.

Download Paper
Paper Id : IJRASET56237
Publish Date : 2023-10-20
ISSN : 2321-9653
Publisher Name : IJRASET
DOI Link : Click Here
 Submit Paper Online
Submit Paper Online

